Interventional procedures for liver abscess and liver biopsies are commonly performed by interventional radiologists or gastroenterologists with specialized training. These procedures offer minimally invasive alternatives to traditional open surgeries and provide diagnostic and therapeutic options for various liver conditions.
Liver Abscess Drainage: If a liver abscess is present, an interventional procedure may be performed to drain the abscess and remove infected material. This is typically done under image guidance, such as ultrasound or CT scan, to precisely locate the abscess. A needle or catheter is inserted through the skin and into the abscess cavity to drain the pus or fluid. Sometimes, a drainage catheter is left in place for continued drainage and administration of antibiotics.
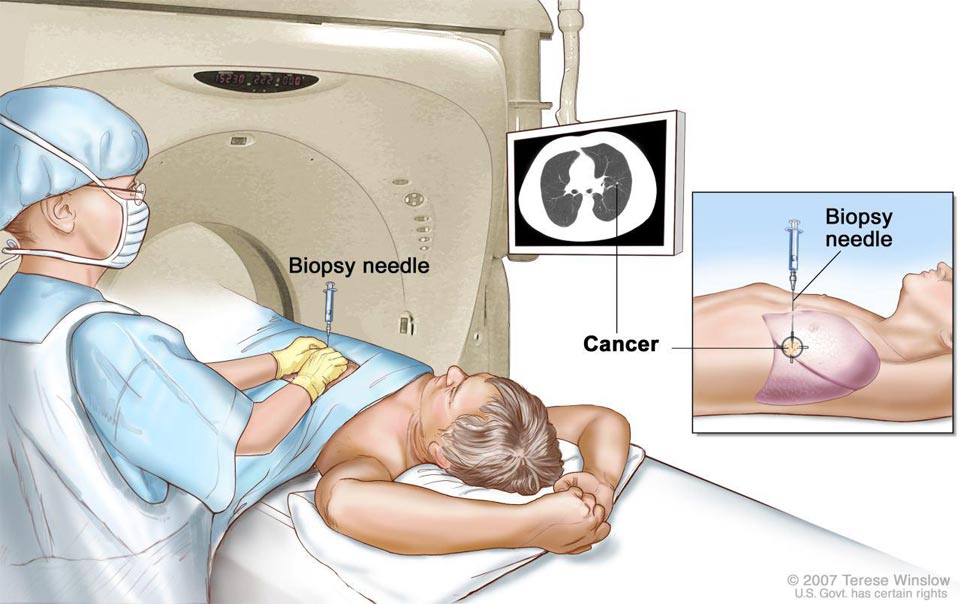
Liver Biopsy: A liver biopsy involves the removal of a small sample of liver tissue for diagnostic purposes. It helps in evaluating liver diseases such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, or liver tumors. There are different methods for liver biopsy, including percutaneous (through the skin), transjugular (through the jugular vein), or laparoscopic approaches. The choice of method depends on the specific situation and the patient’s condition.
During a percutaneous liver biopsy, a needle is inserted through the skin and into the liver to obtain a tissue sample. This is often performed under local anesthesia and image guidance, such as ultrasound, to ensure accurate placement of the needle.